In the digital age, businesses and individuals alike are increasingly relying on cloud-based solutions to manage their data and applications. Cloud-based hosting has emerged as a transformative force in digital infrastructure, offering unprecedented flexibility, scalability, and efficiency. This article delves into the future of digital infrastructure with a focus on cloud-based hosting, exploring its benefits, challenges, and evolving trends. Whether you’re a business owner, IT professional, or technology enthusiast, understanding cloud-based hosting is crucial for staying ahead in a rapidly changing technological landscape.
1. What is Cloud-Based Hosting?
Definition and Overview
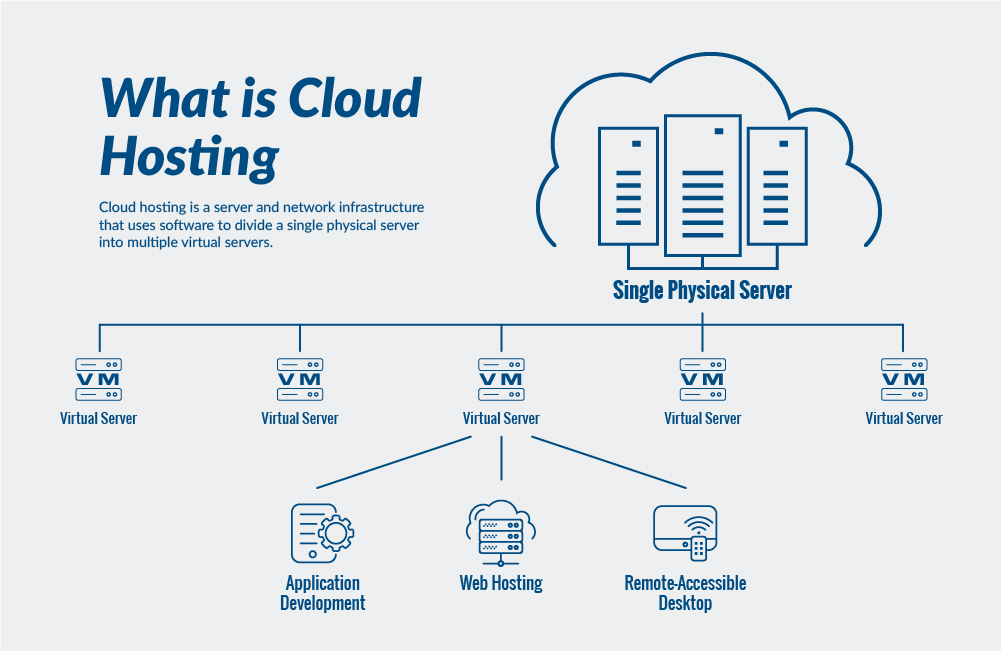
Cloud-based hosting refers to the practice of hosting websites, applications, and data on virtual servers that rely on cloud computing technology. Unlike traditional hosting methods, which utilize physical servers located in data centers, cloud hosting distributes resources across a network of interconnected servers. This approach allows for greater flexibility, scalability, and reliability.
Key Components of Cloud-Based Hosting
- Virtual Servers: The core component of cloud hosting, providing scalable and flexible computing resources.
- Data Centers: Facilities housing the physical servers that power cloud-based services.
- Cloud Storage: A method for storing data on remote servers accessible via the internet.
- Cloud Management Tools: Software solutions for managing and optimizing cloud resources.
The Evolution of Cloud-Based Hosting
Early Developments in Cloud Computing
The concept of cloud computing dates back to the early 2000s when companies like Amazon and Google began offering cloud-based services. Initially, these services were limited in scope but laid the groundwork for the development of more advanced cloud hosting solutions.
The Rise of Cloud Providers
Cloud hosting gained significant traction with the advent of major cloud service providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These providers introduced a range of services, from Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) to Platform as a Service (PaaS), catering to diverse business needs.
Recent Advancements and Trends
In recent years, cloud hosting has evolved with the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and edge computing. These advancements have enhanced cloud-based hosting capabilities, making it more efficient and adaptable to modern requirements.
3. Benefits of Cloud-Based Hosting
Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud-based hosting offers unparalleled scalability, allowing businesses to easily adjust their resources based on demand. This flexibility is particularly advantageous for handling traffic spikes and growing workloads.
Cost-Efficiency
One of the primary benefits of cloud hosting is its cost-efficiency. Businesses pay only for the resources they use, eliminating the need for large upfront investments in physical infrastructure.
Enhanced Reliability and Uptime
Cloud hosting providers typically offer high levels of reliability and uptime through redundant systems and geographic distribution. This ensures that applications and data are accessible even in the event of hardware failures or other issues.
Improved Security and Compliance
Leading cloud providers invest heavily in security measures to protect data and applications. Features such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits contribute to a robust security posture.
Global Accessibility
Cloud-based hosting allows users to access their applications and data from anywhere in the world. This global accessibility is crucial for businesses with a distributed workforce or international clientele.
Challenges and Considerations in Cloud-Based Hosting
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
While cloud providers implement stringent security measures, data privacy remains a significant concern. Businesses must comply with GDPR and HIPAA regulations when storing and processing sensitive information.
Vendor Lock-In
Vendor lock-in occurs when businesses depend on a specific cloud provider’s technology and services, making switching providers or migrating data challenging.
Performance and Latency Issues
Performance and latency can vary depending on the cloud provider and the geographic location of data centers. Businesses should consider these factors when selecting a cloud hosting solution.
Cost Management
While cloud hosting can be cost-effective, it requires careful management to avoid unexpected expenses. Businesses should monitor usage and optimize resource allocation to control costs.
The Future of Cloud-Based Hosting
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are transforming cloud-based hosting by enabling predictive analytics, automated resource management, and enhanced security measures. These technologies will continue to shape the future of cloud hosting.
The Growth of Edge Computing
Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source rather than in centralized data centers. This approach reduces latency and improves performance, making it a key trend in the future of cloud hosting.
The Expansion of Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments
Hybrid and multi-cloud environments combine public and private clouds to offer greater flexibility and resilience. This approach allows businesses to leverage the strengths of different cloud providers and manage workloads more effectively.
Advances in Cloud Security
As cyber threats evolve, cloud providers will continue to enhance their security measures. Innovations such as advanced threat detection, zero-trust architectures, and quantum encryption will play a crucial role in safeguarding cloud-based systems.
The Impact of Regulations and Compliance
The regulatory landscape for cloud computing is continually evolving. Businesses will need to stay informed about changes in regulations and ensure compliance with data protection and privacy laws.
How to Choose the Right Cloud-Based Hosting Provider
Assessing Your Needs
Before selecting a cloud provider, assess your business’s specific needs, including resource requirements, performance expectations, and budget constraints.
Comparing Providers
Evaluate cloud providers based on service offerings, pricing, reliability, and customer support. Consider conducting a proof of concept to test the provider’s services.
Reviewing Security and Compliance Measures
Ensure that the cloud provider’s security and compliance measures align with your business’s requirements. Review their certifications, audits, and data protection practices.
Evaluating Support and SLAs
Check the provider’s support options and service level agreements (SLAs) to ensure they meet your business’s needs for responsiveness and uptime guarantees.
7. Conclusion
Cloud-based hosting has revolutionized digital infrastructure, offering businesses and individuals unprecedented flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, the future of cloud-based hosting promises even more innovations and opportunities. By understanding the benefits, challenges, and trends in cloud hosting, you can make informed decisions that drive your digital strategy forward.